- Call us!
- +86 531 8887 6213
- cathy@winner-psa.com
Each particle size measurement method is to measure a certain physical property of particles under different datum, and different average results can be obtained according to a variety of different methods (such as D [4,3],D [3,2], etc.), but which average particle size should be used? Take a simple example of two spheres with diameters of 1 and 10. For the metallurgical industry, if you calculate a simple number of average particle diameters, the result is D [1,0] =(1+10)/2=5.5. But if you're interested in mass of matter, and mass is a cubic function of diameter, then a sphere of diameter 1 has a mass of 1, and a sphere of diameter 10 has a mass of 1000. In other words, the large sphere makes up 99.9% of the total mass of the system. In metallurgy, only 0.1% of the total mass is lost if a sphere with a particle size of 1 is dropped. Therefore, the simple number average can not accurately reflect the mass of the system, but D [4,3] can better reflect the average mass of particles.
In the example of the two spheres above, the mass matrix volume mean particle size is calculated as follows:
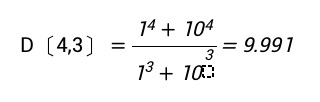
This value is a fairly adequate indication of the quality of the system ,which is important for some industries.
But in a clean room making large-scale integrated circuits, the number or concentration of particles is all that matters, because if a particle falls on a silicon chip, a defect will occur and the product may fail. A method that can directly measure the number or concentration of particles is needed. For particle counting, the number of particles is sufficient; in this case, the size of the particles is not important.
Copyright © Jinan Winner Particle Instrument Stock Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved | Sitemap
Keywords:
Laser Particle Size Analyzer Spray Particle Size Analyzer Particle Image System Online Particle Size Analyzer Particle Size Analyzer particle size distribution particle size analyzer manufacturer Laser diffraction particle size analyzer particle size malvern particle size analyzer